Projects developed with SensEdu
The following section documents select projects developed by SensEdu contributors. These real-world examples demonstrate practical use cases of the platform and highlight its capabilities.
Currently, this section is the main focus of our team. We aim to expand our collection of polished, fully documented projects to better illustrate SensEdu applications. Contributions are highly welcomed! If you’ve created a nice project, please consider adding it to both this wiki and our main repository by following these guidelines.
Most of the projects utilize SensEdu library, but it is not explicitly necessary, you can develop projects with standard or other custom Arduino GIGA R1 libraries.
As detailed in the PCB specifications, all applications center around three core hardware components:
- MEMS microphones
- Barometric Air Pressure Sensor
- Ultrasonic Transducers
Project Development Electronics
Ultrasonic Transceiver
SensEdu’s primary functionality lies in its ultrasonic transceiver capabilities. The system pairs 33 kHz ultrasonic transmitters (speakers) with high-sensitivity MEMS microphones optimized for 10-100 kHz reception (33 kHz resonant frequency). This combination enables implementations such as:
- Distance measurements
- Collision avoidance systems
- Robotic navigation
- Radars
- Radio communication
Barometric Pressure Sensor
Moreover, the board is equipped with a barometric sensor which enables atmospheric measurements. It could be utilized for:
- Elevation tracking (climbing\descent detection)
- Environmental monitoring systems
- Motion pattern recognition (e.g., falling)
- Robot vertical navigation
General Purpose Instrumentation Amplifiers
SensEdu is equipped with extra x2 dual-channel amplifiers AD8222. Their inputs are wired to headers, making them suitable for any application that requires a simple Amplification → ADC signal path. This is the final piece that makes SensEdu an excellent tool for basic sensor systems education, enabling a wide range of projects such as:
- Various bio-signals projects, e.g., Electromyography (EMG)
- Strain Gauge Measurements
- Thermocouple Measurements
Project Examples
Some of the projects already done using SensEdu transducer:
Pulse-Echo Ranging
Measuring distances using ultrasonic pulses and TOF technique - time it takes for the pulse to go from the transducer, reflect off of an object and come back to the receiver. This technique is especially useful for measuring longer ranges. This basic principle is used in not so basic missions like space exploration, forestry and agriculture, surveillance systems, and more!
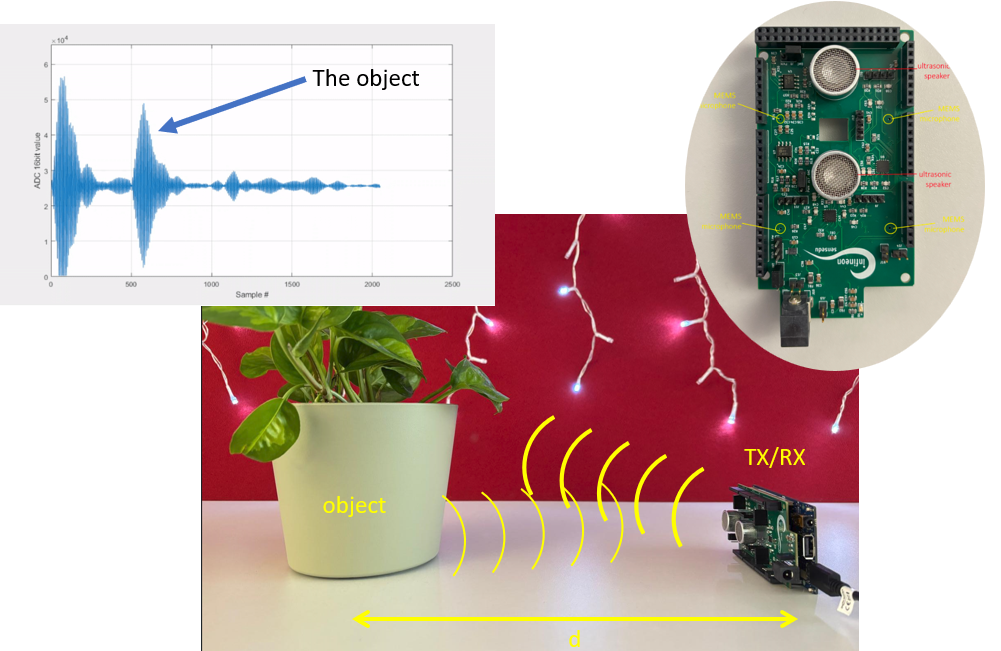
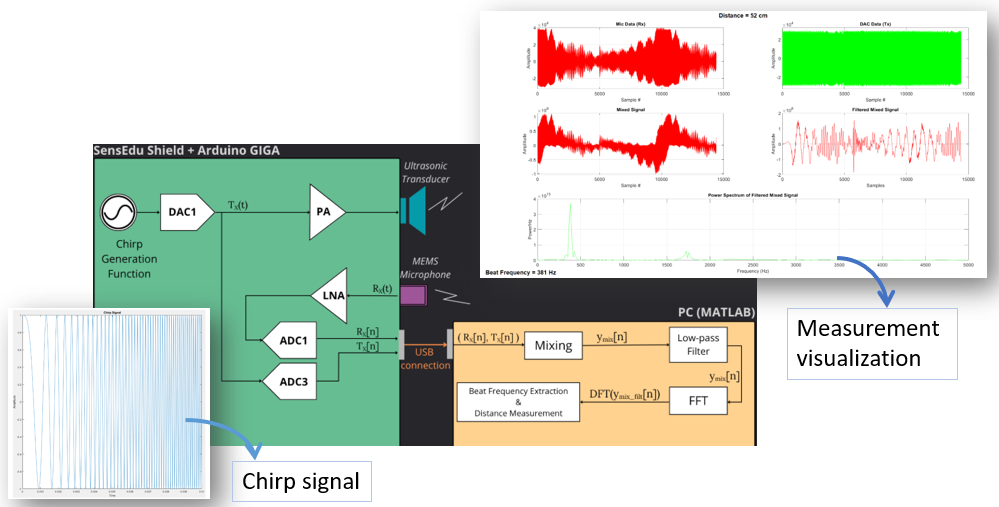
FMCW Ranging
Another popular technique for distance measuring is using frequency modulated continuous wave. It focuses on measuring difference in frequency between the transmitted wave and the received wave. Unlike pulse-echo ranging, this techniqe is particularly useful for measuring small distances with high precision. Understanding this concept is a starting point in understanding how self-driving cars “see” the road or how drones navigate very tight spaces.
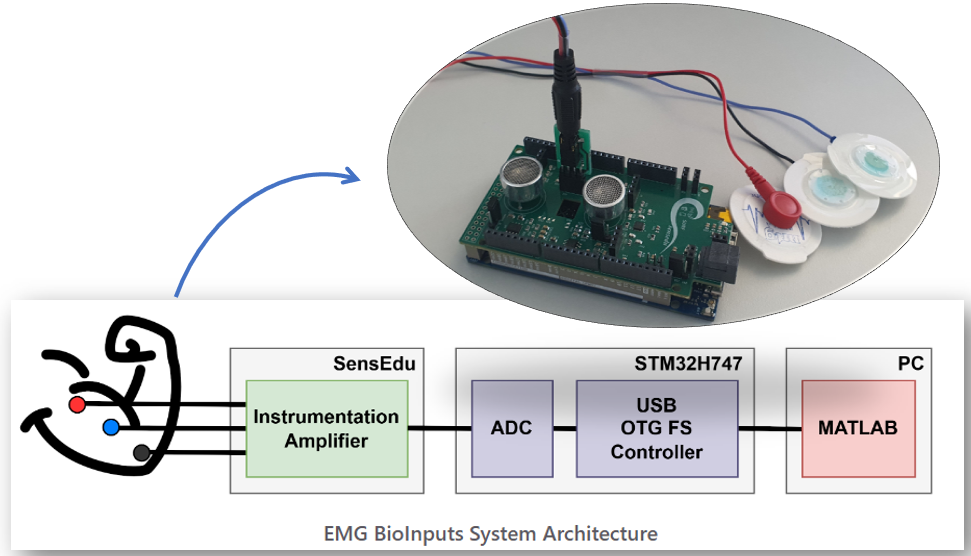
EMG Bioinputs
Playing games is a lot of fun, but playing games using your muscle contractions is even more exciting! By utilizing the electrical signals from muscle contractions, measuring them with the SensEdu board, and following the necessary processing steps, you can achieve this while also learning more about biology!
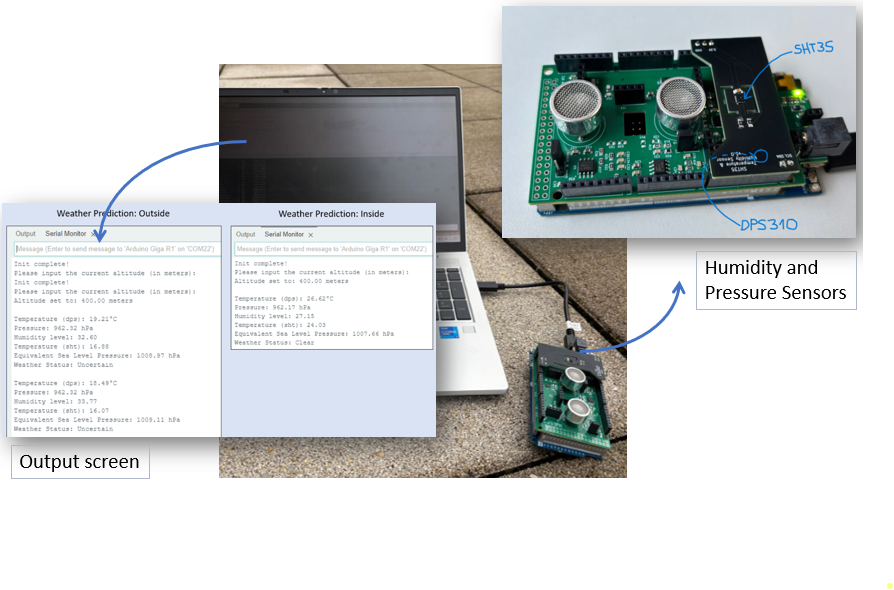
Weather Station
The simplest weather prediction can be established by having information about temperature, pressure and humidity. Using SensEdu pressure sensor and a humidity sensor achieves a simple weather forecast.